
The Periodic Table of Elements helps us better understand chemical elements and their relationship to one another. Metalloids have unique conductivity properties, which make them useful in the semiconductor and computer chip industries.

Some nonmetals are liquids, some are gases. Nonmetals have properties opposite of the metals – they are brittle, not flexible and not strong conductors of heat or electricity.

They share similar characteristics – most are solid, shiny, good conductors of electricity and malleable. Most of the elements on the periodic table are considered metals.One way to sort the elements is to divide them into three categories: metals, nonmetals and metalloids: The periodic table helps chemists classify elements by properties and similarities.
#Periodic table of elements atomic weight how to
10 How to read and interpret the periodic table: 9 IUPAC last updated the periodic table in 2016, adding four new elements: Nihonium (Nh), Moscovium (Mc), Tennessine (Ts) and Oganesson (Og). The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) maintains the periodic table and sets criteria for new additions. 8 For example, elements that have similar properties to sodium (Na), such as Lithium (Li) and Potassium (K), are included in the same family. 7 Chemical element families have similar properties, such as their electron configurations. “Families” are the element groups featured in nine of the 18 vertical columns in the periodic table. Valency is an important aspect of calculating chemical formulas for students and chemists. 6 This is the ability of an atom or a group of atoms to form chemical bonds with other atoms. Once you know the number of electrons of a chemical element, you can calculate its valency. All elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells but have different numbers of electrons and protons. In each period, the elements’ atomic numbers increase from left to right. The periodic table contains seven periods 5 (nine if you count the lanthanides and actinide series). The horizontal rows across the periodic table are called periods. Because atoms naturally occur with different numbers of neutrons-known as isotopes-the atomic mass is an average of all weights of all isotopes for a given atom. Under the element symbol is the atomic weight, which is the average weight of the protons and neutrons in an atom. 4 The atomic number, located at the top left of the element symbol, signifies the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus. How elements are organized on the periodic table:Įlements are organized in horizontal rows by increasing atomic number. 2 Oxygen (O) is the most common element in the Earth’s crust. Today, the 118 chemical elements identified on the periodic table include the materials that make up all known objects in the universe.ĭid you know? The most abundant element (by mass) making up Earth3 is Iron (Fe). He anticipated others would one day be discovered, so he left open spaces in his table for additions. Mendeleev’s periodic table included 63 elements.
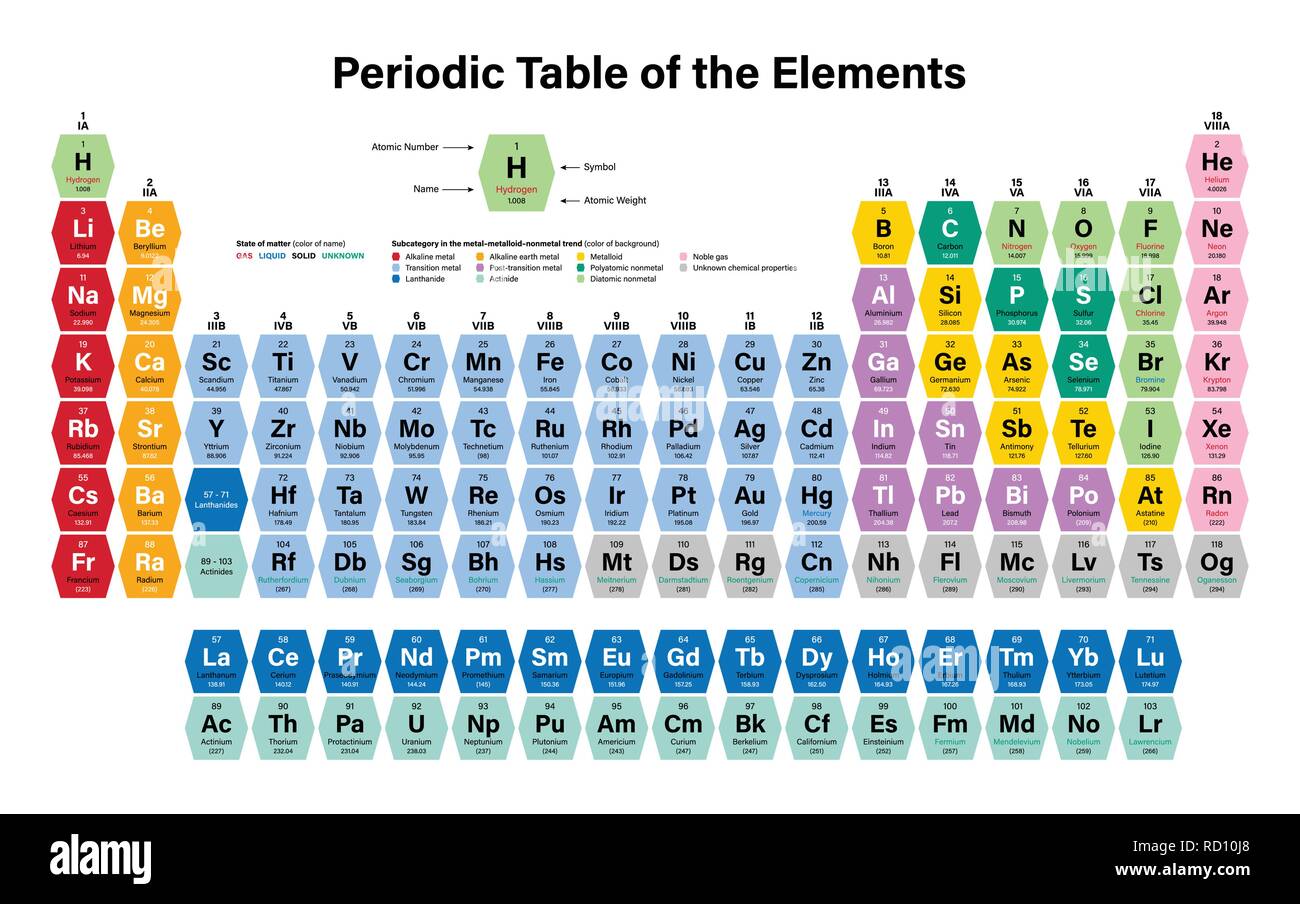
This structure helped Mendeleev and other scientists identify similarities and differences among elements to help predict future chemical reactions. He found a pattern, listing elements by their increasing atomic number and arranging them in a chart-creating the first periodic table. In 1869, Russian chemist Dimitri Mendeleev wanted to see if there was a pattern to the chemical properties of the elements he knew.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
